Clinician perception of the relationship between mental health, health-related social needs, and diabetes outcomes [Diabetes and endocrine disease]
Annals of Family Medicine
NOVEMBER 20, 2024
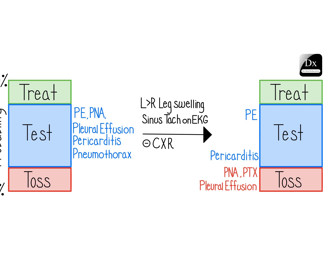
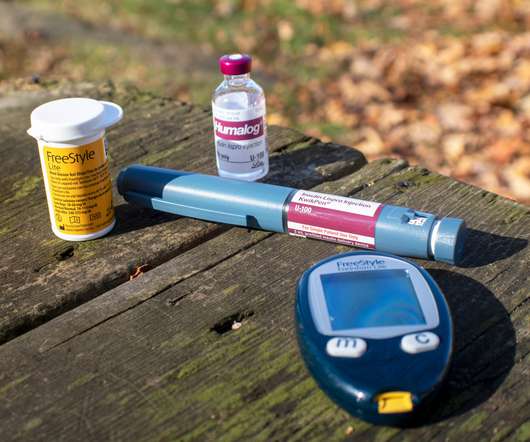
Context: Health-promoting behaviors are crucial for good outcomes in diabetes. Addressing mental health and HRSNs can improve diabetes outcomes, but stigma surrounding these issues can make both patients and providers uncomfortable during clinical discussions. Intervention/Instrument: Semi-structured interview guide.











































Let's personalize your content