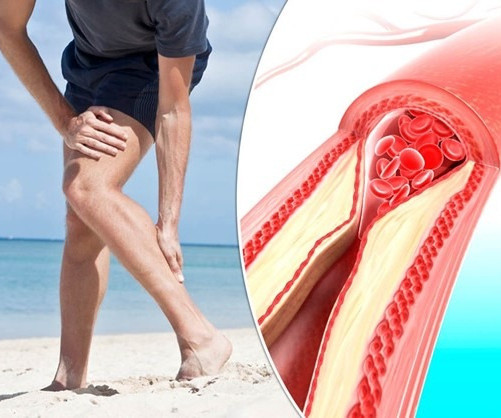
What Happens if Peripheral Arterial Disease is Left Untreated?
Vascular Physician
DECEMBER 21, 2022
Because of this, it is important to address vascular complications as soon as they arise, including Peripheral Arterial Disease (PAD). Early detection can lead to a more comfortable and effective treatment plan. If left untreated, PAD may progress over time and can lead to more serious health complications.











Let's personalize your content